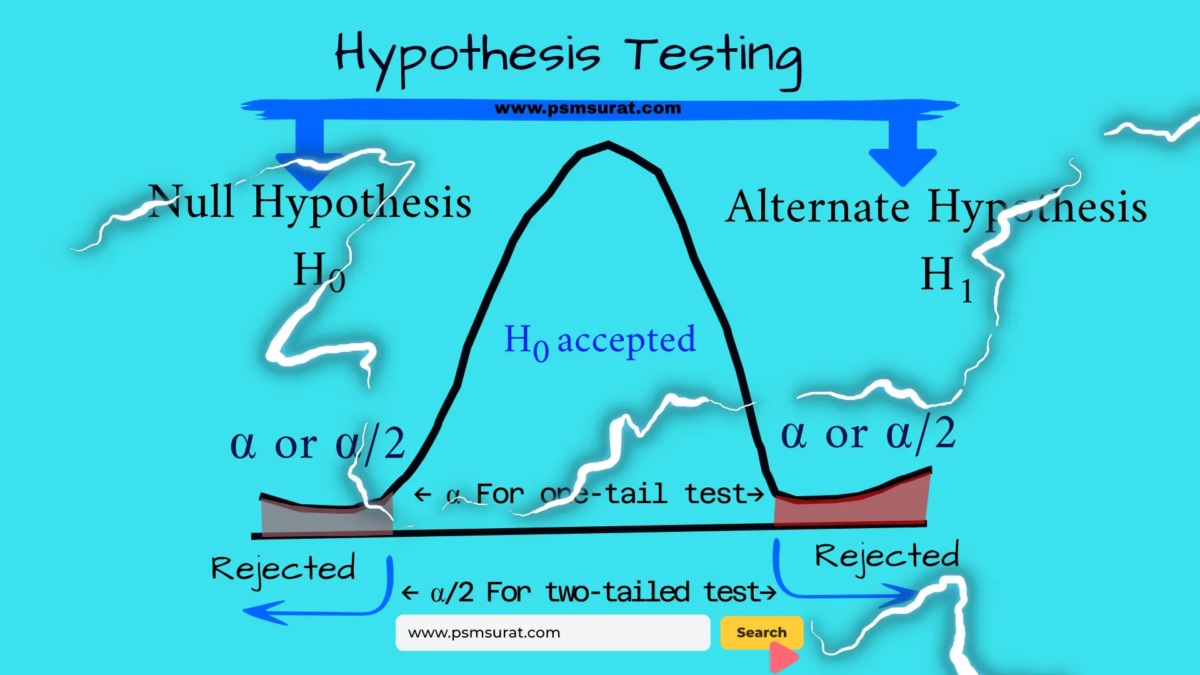
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used in data science to determine whether a hypothesis about a population parameter is true or false.
Probability in Statistics: Types of Probability Distributions Examples and Characteristics
In probability and statistics, a distribution is a function that describes the likelihood of different outcomes in a random event. Simply, it is a frequency plotted as a graph or shown as a table.
Descriptive Statistics & Inferential Statistics: How to Answer to Statistical Exercise in five Steps
In this article, we will discuss how to attempt such a statistical exercise in simple easy steps and answer it correctly.
Epidemiology: What is Bias, Chance, and Confounders in Epidemiology?
Amidst the confusion created by confounders and other factors not obviously causing the disease, epidemiologist use statistics and derive conclusions using p-value or probability which measure chance!
Probability Bay’s theorem: Surprisingly Easy To Understand
Bayes’ theorem is a fundamental concept in probability theory that describes the relationship between the probability of an event occurring (the prior probability) and the probability of that event occurring given certain evidence (the posterior probability). The theorem is named after Thomas Bayes, an 18th-century statistician and theologian who first published the theorem in his 1763 essay “An Essay Towards Solving a Problem in the Doctrine of Chances.”
The theorem is expressed mathematically as:
P(A|B) = P(B|A) * P(A) / P(B)
Where:
- P(A|B) is the probability of event A occurring given that event B has occurred (the posterior probability)
- P(B|A) is the probability of event B occurring given that event A has occurred (the likelihood)
- P(A) is the probability of event A occurring (the prior probability)
- P(B) is the probability of event B occurring (the marginal likelihood or the normalizing constant)
The theorem is used to update the probability of an event occurring based on new information or evidence. It can be used in a wide range of applications, including decision-making, machine learning, natural language processing, and medical diagnosis.
It is important to note that Bayes’ theorem is based on the assumption of conditional independence, which means that the probability of an event occurring is not affected by the occurrence of other events.