Water pollution is a growing problem that affects our planet. It can occur due to a range of factors, from human activities to natural causes. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of water pollution, including its causes, effects, and possible solutions.
Join me as we dive into the world of water pollution and explore its causes, consequences, and solutions. From individual actions to community initiatives, we can all play a role in preventing water pollution and protecting the health and well-being of our planet. Get ready to be inspired, and motivated to make a difference.
A Glass of Water

Have you ever stopped to consider the quality of the water you drink, swim in, or use in your daily life?
Unfortunately, water pollution is a serious and growing problem around the world, with devastating effects on our environment, health, and economy.
From toxic chemicals and plastic waste to agricultural runoff and sewage, there are countless sources of water pollution that threaten our freshwater and marine ecosystems.
What Is Water?
“What is water? It’s the same water that our grandfathers saw in rivers, that our fathers saw in wells and lakes, that we see in taps, and that our children now see in water bottles. But will the children of our children even be able to see water at all?”

Water Most Important Building Blocks for Life!

Every now and then we hear NASA or some other agency gathering pieces of evidence of water on other planets. One of the most important reasons is that water is essential for life as we know it. Wherever water is found, there is the possibility of finding life or the conditions necessary to support life.
Water is one of the most important building blocks for life whether it is on this planet or any other planet in the future.
Water Pollution Overview
Water, the source of life and the elixir of our planet is a precious resource that sustains us all. From the oceans to the rivers, from the glaciers to the groundwater, water is essential to our survival and the survival of all living beings. However, despite its immense importance, water is becoming increasingly scarce and polluted, putting at risk our health, our environment, and our future.
Water and Survival
About 71% of the Earth’s surface is covered by water, but only about 2.5% of that is freshwater that is accessible for human use.
The human body is made up of approximately 60% water. The brain and heart are composed of 73% water, while the lungs are about 83% water.
Water is essential for many bodily functions, including regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients and oxygen, and removing waste.
Water Pollution & Water Scarcity Dual Challange

Water scarcity affects over 2 billion people worldwide, and this number is expected to increase due to population growth, climate change, and increasing demand for water.
Agriculture accounts for about 70% of global freshwater withdrawals, making it the largest user of water.
Many species of plants and animals are adapted to specific water conditions, and changes in water availability and quality can have significant impacts on ecosystems.
These data points highlight the critical role that water plays in sustaining life and the urgent need to conserve and protect this precious resource.
What Is Water Pollution?
Water pollution happens when harmful substances, frequently chemicals or microorganisms, invade and taint a body of water such as a river, stream, lake, ocean, aquifer, or other water sources, deteriorating the quality of water and making it toxic to both humans and the environment.
How Significant Water Pollution is?
The issue of water pollution is posing a significant threat to our well-being. The use of contaminated water is responsible for a greater number of deaths annually than all types of violence and wars put together. Additionally, our sources of clean and drinkable water are limited, with less than 1% of the world’s freshwater being accessible to us. Unless we take measures to address this problem, the situation will become more challenging by 2050, with global demand for freshwater projected to increase by one-third. The Worldwide Fund for Nature (WWF) has identified 100 cities, including 30 in India, that will face severe water crises by 2050.
Water A ” Universal Solvent” Susceptible to Water pollution
Water has a unique susceptibility to pollution. As a “universal solvent,” it has the ability to dissolve a greater range of substances than any other liquid on the planet. This property is responsible for the creation of colorful beverages like Kool-Aid and mesmerizing blue waterfalls. However, it also makes water highly susceptible to pollution, as hazardous substances from industrial, agricultural, and urban areas easily dissolve and mix with it, leading to water pollution.
Cause Or Saurce Of Water Pollution
Sewage and Wastewater
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in India has reported that around 70% of the water pollution in India is caused by untreated domestic sewage, and this untreated wastewater is often discharged directly into rivers, lakes, and other water bodies, leading to serious health and environmental problems. The problem is particularly acute in urban areas, where the rapid growth of population and inadequate infrastructure have led to a huge increase in the amount of untreated wastewater being generated.

Agricultural
The agricultural sector not only consumes the largest amount of global freshwater resources, accounting for roughly 70 percent of the earth’s surface water supplies for farming and livestock production, but it is also a significant contributor to water pollution worldwide. Agriculture is the primary cause of water degradation, and it heavily contaminates estuaries and groundwater. When it rains, fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste from farms and livestock operations wash nutrients and pathogens such as bacteria and viruses into our waterways. Nutrient pollution, caused by excessive nitrogen and phosphorus in water or air, poses the most significant threat to water quality globally, leading to a toxic mix of blue-green algae that can be detrimental to both humans and wildlife.
Industrial and trade waste

While major oil spills often grab headlines, the reality is that consumers are responsible for the vast majority of oil pollution in our oceans. This includes the oil and gasoline that seeps from millions of cars and trucks every day. Additionally, almost half of the approximately 1 million tons of oil that enter marine environments annually originates from sources on land such as factories, farms, and cities. Tanker spills only account for roughly 10 percent of the oil found in oceans worldwide, whereas one-third comes from regular shipping industry operations, including both legal and illegal discharges. Furthermore, fractures known as seeps release oil naturally from under the ocean floor.
Physical Pollutants
Radioactive contaminants that are accidentally released or improperly disposed of pose a serious threat to groundwater, surface water, and marine resources. These contaminants come from various sources such as uranium mining, nuclear power plants, and the production and testing of military weapons. Even universities and hospitals that use radioactive materials for research and medicine can contribute to the generation of such contaminants.
Categories Of Water Pollution
Point source pollution
Point source pollution is the term used when pollution stems from a single source. This can include legally or illegally discharged wastewater (known as effluent) from manufacturers, oil refineries, or wastewater treatment facilities. Other examples are contamination from septic systems that are leaking, illegal dumping, and chemical, and oil spills.
Nonpoint source
Nonpoint source pollution is contamination derived from diffuse sources. These may include agricultural or stormwater runoff or debris blown into waterways from land.
Transboundary
It goes without saying that water pollution can’t be contained by a line on a map. Transboundary pollution is the result of contaminated water from one country spilling into the waters of another.
Types of Water Being Impacted Due to Water Pollution
It is crucial for us to know which type of water is most affected.
Groundwater Pollution
When rain falls and seeps deep into the earth, filling the cracks, crevices, and porous spaces of an aquifer (basically an underground storehouse of water), it becomes groundwater—one of our least visible but most important natural resources.
Groundwater gets polluted when contaminants—from pesticides and fertilizers to waste leaching from landfills and septic systems—make their way into an aquifer, rendering it unsafe for human use.
According to a report by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation, around 85% of rural households and 50% of urban households in India depend on groundwater for their daily needs. Groundwater is a critical source of water for irrigation and industries in India, and its over-exploitation has led to a decline in water levels in many areas.
Surface Water Pollution
गंगा सिंधु सरस्वती च यमुना गोदावरी नर्मदा ।
कावेरी शरयू महेन्द्रतनया चर्मण्वती वेदिका ।।
क्षिप्रा वेत्रवती महासुरनदी ख्याता जया गण्डकी ।
पूर्णाःपूर्णजलैःसमुद्रसहिताःकुर्वन्तु मे मंगलम् ।।
It is unfortunate that in spite of worshiping the river as a mother and goddess in our country, we are indifferent to their maintenance and safeguarding. People do all kinds of activities with rivers from defecating at the banks to releasing harmful chemicals.
Surface Water Pollution in India
Surface water pollution is a significant problem in India, with many of the country’s rivers and lakes being contaminated by a range of pollutants. Some of the main sources of surface water pollution in India include industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, untreated sewage, and solid waste dumping.
According to a study by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), around 60% of India’s water sources are polluted. The study found that 302 of the 351 polluted river stretches in India were critically polluted. The most polluted rivers in India include the Ganga, Yamuna, and Sabarmati. The main pollutants in these rivers are sewage, industrial waste, and agricultural runoff.
The impacts of surface water pollution in India are significant, including the spread of waterborne diseases, reduced access to safe drinking water, and negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems. The Indian government has taken steps to address surface water pollution, including the Clean Ganga Mission and the National River Conservation Plan, but much more needs to be done to protect the country’s water resources.
Ocean Water Pollution
Most of the ocean pollution, about 80%, has its origins on land, whether near the coast or far inland. Pollutants such as heavy metals, nutrients, and chemicals are transported by streams and rivers from farms, factories, and urban areas into bays and estuaries, eventually flowing out into the sea. Plastic, especially marine debris, is carried in by the wind or enters via storm drains and sewers. In addition, oil spills and leaks of all sizes can also contaminate our oceans. Moreover, the ocean is persistently absorbing carbon pollution from the atmosphere, with man-made carbon emissions being responsible for up to a quarter of it.
Indicators Of Water Pollution
Are there any indicators that can tell us that water is being polluted?
The indicators of pollution include the amount of total suspended solids and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) at 20 deg. C, the concentration of chlorides, nitrogen, and phosphorus, and the absence of dissolved oxygen.
Effects Of Water Pollution
Let us first look at the WHO factsheet on drinking water:
- Over 2 billion people live in water-stressed countries, which is expected to be increased in some regions as a result of climate change and population growth.
- Globally, at least 2 billion people use a drinking water source contaminated with faeces. Microbial contamination of drinking water as a result of contamination with faeces poses the greatest risk to drinking water safety.
- While the most important chemical risks in drinking water arise from arsenic, fluoride, or nitrate, emerging contaminants such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs), and microplastics generate public concern.
- Safe and sufficient water facilitates the practice of hygiene, which is a key measure to prevent not only diarrhoeal diseases but acute respiratory infections and numerous neglected tropical diseases.
- Microbiologically contaminated drinking water can transmit diseases such as diarrhea, cholera, dysentery, typhoid, and polio and is estimated to cause 485 000 diarrhoeal deaths each year.
- In 2020, 74% of the global population (5.8 billion people) used a safely managed drinking-water service – that is, one located on premises, available when needed, and free from contamination.
Water Related Diseases
Man’s health may be affected by the ingestion of contaminated water either directly or through food; and by the use of contaminated water for purpose of personal hygiene and recreation. The term water-related diseases include classical water-borne diseases. Developing countries carry a heavy burden of water-related diseases, the heaviest being diarrhoeal diseases. Water-related diseases may be classified as Biological or water-borne diseases caused by bacteria and viruses and chemicals due to the presence of chemicals in it.
Water Born Diseases Due to the Presence of Infective Agents
The water-borne disease is again classified as per the presence of an infective agent or aquatic host. Disease caused by the presence of infective agents as follows:
Virus
viral hepatitis A, hepatitis E, poliomyelitis, and rotavirus diarrhea in infants.
Bacterial
Bacterial typhoid and paratyphoid fever, bacillary dysentery, E coli diarrhea, cholera
Protozoal
Protozoal amoebiasis and giardiasis
Helminthic
Helminthic roundworm, threadworm, and hydatid disease
Diseases caused by the presence of aquatic hosts
Diseases caused by the presence of aquatic hosts include schistosomiasis due to the presence of snails and guinea worms and fish tapeworms due to the presence of cyclops in the water.
Chemical
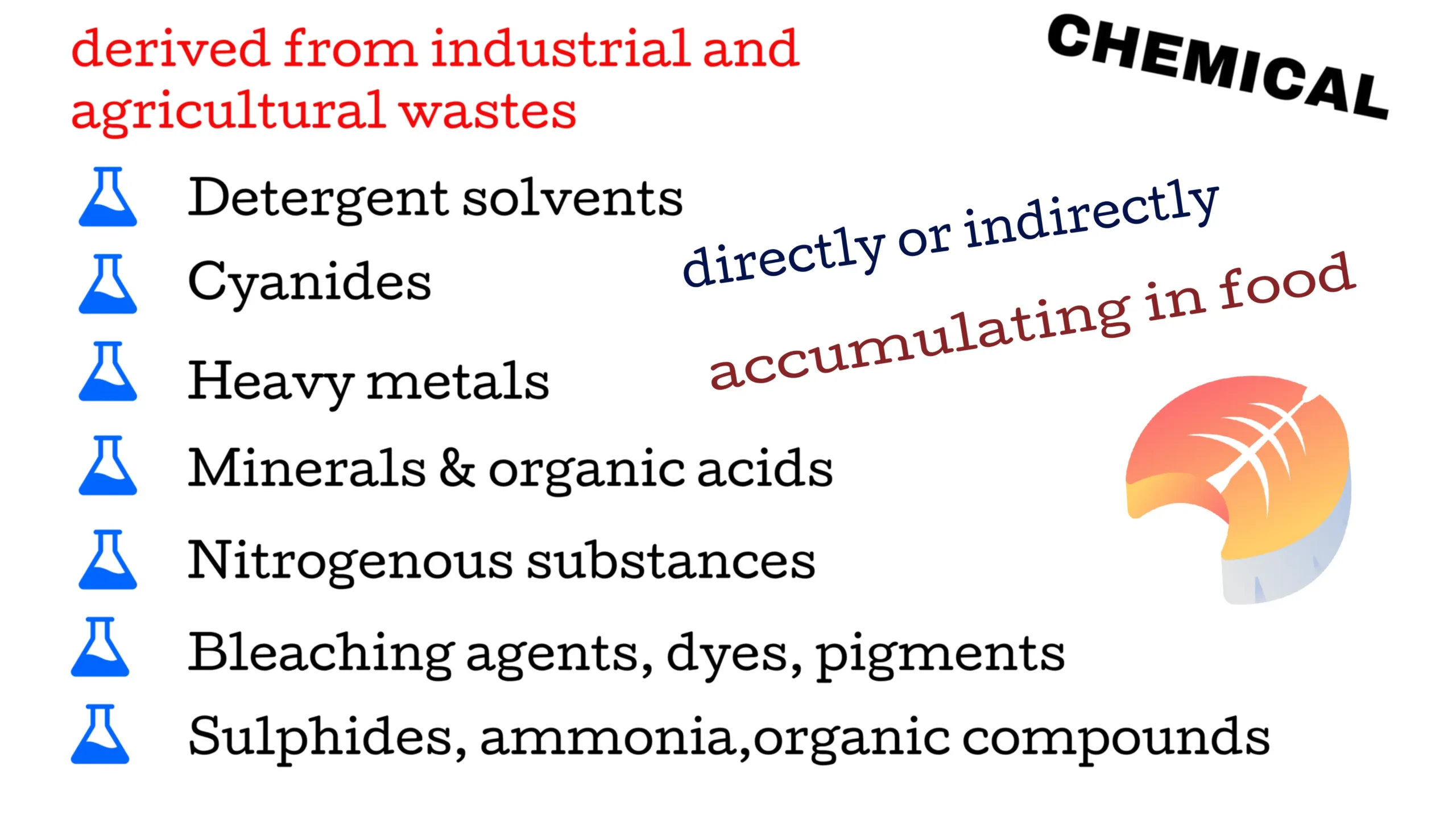
Chemical pollutants of diverse nature derived from industrial and agricultural wastes are increasingly finding their way into public water supplies. These pollutants include detergent solvents, cyanides, heavy metals, minerals and organic acids,
nitrogenous substances, bleaching agents, dyes, pigments, sulphides, ammonia, and toxic and biocidal organic compounds of a great variety. Chemical pollutants may affect man’s health not only directly, but also indirectly by accumulating in aquatic life (e.g. fish) used as human food. For example, Minamata disease is caused by methyl mercury due to contaminated fish in Minamata Japan. The present concern about chemical pollutants in water relates not so much to their acute toxic effects on human health as to the possible long-term effects of low-level exposure, which are often non-specific and difficult to detect. Another important thing is some of the new pollutants are not easily removed by conventional water treatment or purification processes.
In many developed countries where water-borne communicable diseases have virtually disappeared, more attention is now being paid to chemical pollution.
Additionally, water also is associated with:
Dental Health
The presence of fluoride at about 1 mg/L in drinking water is known to protect against dental caries, but high levels of fluoride (1.5mg/L) cause mottling of the dental enamel;
Cyanosis in infant
The high nitrate content of water is associated with methemoglobinemia. This is a rare occurrence but may occur when surface water from farmland, treated with fertilizer, gains access to the water supply.
Cardiovascular diseases
The hardness of water appears to have a beneficial effect against cardiovascular diseases;
Other Waterborne Diseases
Some diseases are transmitted because of inadequate use of water like shigellosis, trachoma and conjunctivitis, ascariasis, and scabies. Some diseases are related to the disease-carrying insects breeding in or near water, like malaria, filaria, arboviruses, onchocerciasis, and African trypanosomiasis. While pollution seems to be an inevitable consequence of modern industrial technology, the problem, now, is to determine the level of pollution that permits economic and social development without presenting hazards to health.
Before we talk about what we can do to prevent or control the pollution of water, I want to quote Robin Wall Kimmerer eminent professor of the environment. She said :
“Restoring land without restoring relationship is an empty exercise. It is relationship that will endure and relationship that will sustain the restored land. Therefore, reconnecting people and the landscape is as essential as re-establishing proper hydrology or cleaning up contaminates. It is medicine for the earth.”
— Braiding Sweetgrass by Robin Wall Kimmerer
Isn’t it a part of Indian culture, we have been worshiping nature for centuries.
Solutions To Water Pollution
A. At Individual Levels
There are several things you can do at the individual level to prevent water pollution. Here are some suggestions:
Properly dispose of hazardous materials:
Many household items contain hazardous chemicals that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. Make sure to dispose of items such as batteries, electronics, and cleaning products at a designated hazardous waste collection site.
Reduce your use of plastic:
Plastic waste is a major contributor to water pollution. Reduce your use of plastic by using reusable bags, water bottles, and containers. (Reduce -Reuse and recycle)
Be careful with household chemicals:
Avoid pouring chemicals such as paint, oil, and cleaning products down the drain or toilet. Instead, dispose of these items at a designated hazardous waste collection site.
Use eco-friendly products:
Choose products that are eco-friendly and do not contain harmful chemicals. This includes cleaning products, personal care products, and laundry detergents.
Properly maintain your car:
Cars can release pollutants such as oil, antifreeze, and brake fluid. Make sure to properly maintain your car and dispose of any hazardous materials at a designated collection site.
Support environmentally-friendly policies:
Support policies and initiatives that aim to protect the environment, such as water conservation efforts and regulations on industrial pollution.
B. At the Community level
Water pollution can also be prevented at the community level. Here are some suggestions:
Participate in community clean-up events:
Join community clean-up events to help remove litter and debris from waterways. This can help prevent pollution from entering the water in the first place.
Properly dispose of hazardous waste:
Many communities have designated hazardous waste collection sites where residents can dispose of hazardous materials such as batteries, electronics, and cleaning products.
Encourage water conservation:
Encourage water conservation efforts in your community by promoting the use of low-flow showerheads and toilets, fixing leaks, and reducing water usage in landscaping.
Support local environmental initiatives:
Support local environmental initiatives and organizations that are working to protect waterways and reduce pollution.
Implement pollution prevention programs:
Encourage local businesses to implement pollution prevention programs and reduce their impact on the environment. This can include reducing their use of harmful chemicals, properly disposing of hazardous waste, and implementing water conservation measures.
Implement stormwater management practices:
Encourage the implementation of stormwater management practices in your community, such as green roofs and rain gardens, to help reduce pollution runoff.
Educate others:
Educate others in your community about the importance of preventing water pollution and the steps they can take to make a difference. This can include hosting educational events or sharing information on social media platforms.
It is imperative that we take action to conserve and protect our water resources, not only for ourselves but for generations to come. With every drop of water, we save, we can make a significant difference in the world and create a better future for all. Let us join hands and make water conservation a way of life, a habit that we practice every day, and a legacy we leave for our children and the world.
FAQs On Water Pollution
What is water pollution?
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies such as rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater by harmful substances. These substances can be chemicals, microorganisms, or other pollutants that negatively affect the quality of the water.
What are the causes of water pollution?
Water pollution can be caused by a variety of factors, including industrial waste, sewage, agricultural runoff, oil spills, and littering. Natural phenomena like algae blooms and volcanic eruptions can also contribute to water pollution.
What are the effects of water pollution?
Water pollution can have harmful effects on both the environment and human health. It can kill aquatic life, contaminate food sources, and damage ecosystems. Humans who consume contaminated water can suffer from illnesses, skin irritations, and other health problems.
How can we prevent water pollution?
Preventing water pollution requires a multi-faceted approach that involves reducing the sources of pollution, regulating industrial practices, improving sewage treatment, and promoting the responsible use of resources. Individuals can also help by reducing their water usage, properly disposing of waste, and avoiding the use of harmful chemicals.
What are some examples of water pollutants?
Common water pollutants include heavy metals, pesticides, fertilizers, bacteria and viruses, plastic, oil, and other toxic chemicals.
How does water pollution affect marine life?
Water pollution can be extremely harmful to marine life, causing fish and other aquatic animals to suffer from deformities, reproductive issues, and other health problems. Polluted water can also lead to the destruction of coral reefs, which are important habitats for a variety of marine species.
What can we do to clean up polluted water?
Methods for cleaning up polluted water include using activated carbon filters, bioremediation, and phytoremediation. In some cases, it may also be necessary to remove contaminated sediment or dredge the affected area.
How does water pollution affect human health?
Water pollution can have negative impacts on human health, particularly for those who rely on contaminated water sources for drinking or bathing. Exposure to water pollutants can cause skin irritation, gastrointestinal problems, neurological disorders, and even cancer.
What laws exist to protect against water pollution In India?
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974: This act (CPCB) aims to prevent and control water pollution by regulating and monitoring the discharge of pollutants into water bodies. It establishes central and state pollution control boards to enforce its provisions.
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986: This act provides for the protection and improvement of the environment, including water bodies. It gives the central government the power to take measures to protect and restore the environment and provides for penalties for non-compliance with its provisions.
- The National Green Tribunal Act, 2010: This act provides for the establishment of a specialized tribunal to hear cases related to environmental protection, including water pollution.
- The River Boards Act, 1956: This act provides for the establishment of river boards to regulate the use of water resources, prevent pollution, and promote their proper utilization.
- The Indian Penal Code (IPC): Section 277 of the IPC provides for punishment for fouling water of a public spring or reservoir.
- The Municipal Solid Wastes (Management and Handling) Rules, 2000: These rules regulate the management and disposal of solid waste, including hazardous waste, which can pollute water bodies.
- The Biological Diversity Act, 2002: This act provides for the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity, including water bodies.
What role do industries play in preventing water pollution?
Industries have a significant role to play in preventing water pollution, as many industrial processes produce harmful pollutants that can end up in water sources. Companies can reduce their impact on water quality by implementing sustainable practices, reducing waste, and investing in pollution prevention technologies.

Add a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment