Hello, friends welcome to another article on the climate phenomenon El Nino, in this article we will try to understand the El Nino and La Nina phenomenon, how the Indian monsoon is affected by this phenomenon, and lastly how El Nino imposes risk to our health.
Let us first talk about El nino and La Nina.
Winds: Trade Winds!
To understand El Nino and La Nina we have to first understand the normal wind pattern and the normal circumstances under which normal rain occurs in India and the other parts of the world.

Trade Winds
Trade winds are persistent, steady winds that blow in a particular direction across the Earth’s surface. They are a type of wind that occurs in the tropics, specifically between the equator and about 30 degrees latitude, in both the northern and southern hemispheres. Trade winds are known for their reliability and consistency, and they have historically been used by sailors for navigation. And hence they derived the name trade winds.
What Causes Trade Winds?
The trade winds are caused by the global atmospheric circulation patterns driven by differences in temperature and pressure between the equator and the poles. Near the equator, the warm air rises, creating a low-pressure area, while cooler air from higher latitudes flows toward the equator to replace it, creating a high-pressure area. This results in the trade winds blowing from east to west, from the subtropical high-pressure belts towards the equator, where they converge and rise.
ENSO: El Niño-Southern Oscillation
Trade winds play an important role in shaping weather patterns, ocean currents, and climate around the world. In addition, trade winds can affect phenomena such as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in the Pacific Ocean, which has global climate implications.
ENSO stands for El Niño-Southern Oscillation, which is a climate phenomenon that refers to the cyclic changes in sea surface temperatures, atmospheric pressure, and oceanic and atmospheric circulation patterns in the tropical Pacific Ocean. ENSO is a natural climate variability that typically occurs in an irregular timeframe of 2 to 7 years and has global impacts on weather and climate patterns.
Normal Circumstances In the Absence of El Nino?

Under normal circumstances, there will be hot water in the central regions of the Pacific Ocean similarly the cold water is confined to the coastal margins of Southern America. Moreover, there is a high-pressure region towards the South American side of the South Pacific Oceans and there is a low-pressure region towards the Australian side. We already discussed how wind moves from a higher-pressure region to a lower-pressure region.
So, we can see a wind current moving from higher-pressure to low-pressure regions, this wind current along with it, drags the warmer water towards the Australian side and similarly, it also drags the colder water from the South American coast. We can see here that this warmer water is moving towards the Australian side and increasing its amount. Similarly, the amount of cold water rising on the South American side is known as upwelling which brings nutrient-rich water to this region and it is good for fishing.
Now let’s talk about El Niño-Southern Oscillation.
ENSO has two main phases:
El Niño: “Little Boy”

This phase occurs when sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean become unusually warm, disrupting normal atmospheric and oceanic patterns. El Niño is characterized by weakened trade winds, reduced upwelling of cold nutrient-rich waters in the eastern Pacific, changes in atmospheric pressure patterns, and impacts on global weather patterns, such as changes in precipitation, temperature anomalies, and extreme weather events.
As this phenomenon mostly occurs in this southern hemisphere just right below the equator EL NINO is sometimes also called Southern oscillation.
El Nino Effect On Sea Current: Draughts & Floods
During El Nino, the lower pressure region changes to higher pressure region and the higher pressure region changes to lower pressure region. Earlier there was a lot of rainfall over the Australian and Indonesian regions because the wind currents were rising over there,
but due to El Nino, there is no rain, though the inland parts of Australia witness a severe drought condition, but on the other hand near the Peruvian coast, the warm pool of ocean currents brings heavy rain floods to the American continent.
But Why The Pacific Ocean?

You might be wondering why this phenomenon is happening in the Pacific Ocean, the reason is that The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of the world’s ocean basins. Covering approximately 63 million square miles and containing more than half of the free water on Earth, the Pacific is by far the largest of the world’s ocean basins. All of the world’s continents could fit into the Pacific basin.
La Niña: “Little Girl”

This phase occurs when sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean become unusually cool, leading to opposite effects compared to El Niño. La Niña is characterized by stronger trade winds and enhanced upwelling of cold nutrient-rich waters in the eastern Pacific.
So basically, it is the exaggerated form of usual trade winds and rain patterns.
Frequency of El Niño & La Niña Occurance
El Niño and La Niña episodes typically last nine to 12 months, but some prolonged events may last for years.
In Spanish, El Niño means The Little Boy and La Niña means The Little Girl. In that region it happens in winter but here in India is summer at the same time. While their frequency can be quite irregular, el niño and la niña events occur on average every two to seven years. As per a recent study, this phenomenon will become stronger by 2030.
How Does El Nino Affect The Indian Monsoon?
The normal monsoon in India occurs due to a combination of the following factors:
1. Differential Heating

During summer, the landmass of India heats up more rapidly than the surrounding seas, creating a temperature gradient between the land and the ocean. This causes low pressure to form over the Indian subcontinent, particularly over the northern plains, while high pressure prevails over the Indian Ocean. This temperature difference sets up the monsoonal circulation.
2. Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
The ITCZ, also known as the monsoon trough, is a low-pressure belt that migrates northwards from the southern hemisphere towards the Indian subcontinent during the summer months. As it moves north, it brings with it moisture-laden winds from the Indian Ocean, which converge over the subcontinent, leading to the onset of the monsoon rainfall.
3. Trade Winds
The trade winds from the southern hemisphere, known as the southeast trade winds, blow across the Indian Ocean and are deflected towards the west by the Coriolis effect. These trade winds, combined with the monsoonal circulation and the ITCZ, result in the southwest monsoon winds that bring rainfall to India.
4. Topography

The geography and topography of the Indian subcontinent also play a role in the normal monsoon. The Western Ghats, a mountain range along the west coast of India, acts as a barrier, forcing the moisture-laden winds from the Arabian Sea to rise and cool, resulting in heavy rainfall on the windward side of the mountains.
5. Sea Surface Temperatures
The temperature of the Indian Ocean also affects the normal monsoon in India. Warmer-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the tropical eastern Indian Ocean, near the Indonesian archipelago, can enhance the monsoon rainfall, while cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, known as El Niño, can weaken the monsoon.
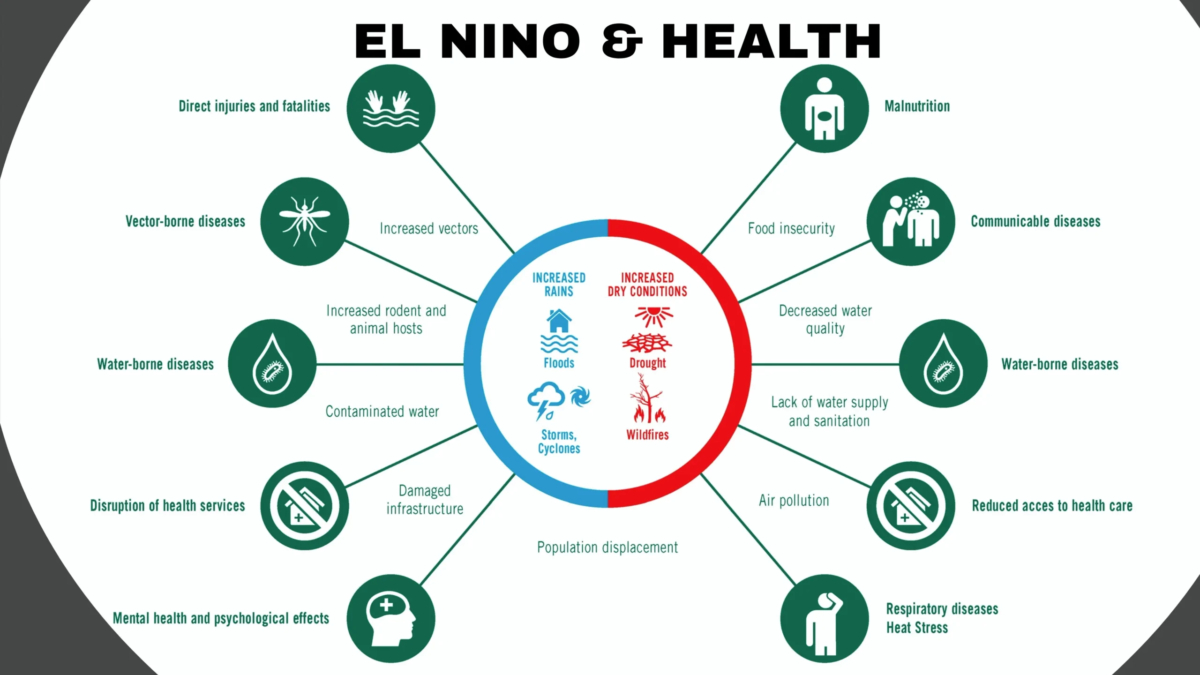
El Nino And Our Health
El Niño can impact human health as follows:

Increase in Infectious Diseases:
El Niño can lead to an increase in the occurrence of infectious diseases, such as dengue fever, malaria, and cholera. This is because the increased rainfall and warmer temperatures associated with El Niño can create ideal breeding conditions for disease-carrying mosquitoes and other insects.

Respiratory Illness:
El Niño can also contribute to poor air quality and an increase in respiratory illnesses, such as asthma and allergies. This is due to the higher temperatures and humidity, which can lead to an increase in air pollution, including smog and smoke from wildfires.
Malnutrition:
El Niño can also result in food insecurity and malnutrition in some areas, as it can cause droughts or floods, which can damage crops and decrease food production.
Mental Health:
El Niño can also have an impact on mental health, particularly in areas that experience extreme weather events, such as floods or hurricanes. These events can lead to displacement, loss of homes, and disruption of daily routines, which can contribute to STRESS, ANXIETY, AND DEPRESSION.
Waterborne Diseases:
El Niño can also increase the risk of waterborne diseases, such as cholera, as it can cause flooding and contamination of water sources.
FAQs
What is El Niño?
El Niño is a complex weather pattern that results from variations in ocean temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, leading to changes in global weather patterns.
How does El Niño affect the Indian monsoon?
El Niño disrupts the normal pattern of monsoon rainfall in India, leading to decreased rainfall and drought conditions in some parts of the country.
Can El Niño cause floods in India?
Yes, El Niño can cause extreme weather events such as floods and heavy rainfall in some parts of India.
How often does El Niño occur in India?
El Niño occurs irregularly in India, typically every 2-7 years.
Does El Niño affect agriculture in India?
Yes, El Niño can have a significant impact on agriculture in India, leading to crop failures and food shortages.
How does El Niño affect ocean currents and marine life in India?
El Niño can disrupt ocean currents and alter water temperatures, leading to changes in marine life populations and biodiversity.
Can El Niño affect air quality in India?
Yes, El Niño can lead to increased air pollution in India due to changes in weather patterns and human activity.
How does El Niño impact public health in India?
El Niño can lead to the spread of diseases such as malaria and dengue fever, as well as malnutrition and other health problems due to drought and food shortages.
Can El Niño be predicted in advance?
Yes, El Niño can be predicted to some extent using advanced weather modeling and monitoring of ocean temperatures.
What can be done to mitigate the effects of El Niño in India?
Strategies for mitigating the effects of El Niño in India include developing drought-resistant crops, improving water management and irrigation, and implementing early warning systems for extreme weather events.
#ElNino #ClimatePhenomenon #WeatherPattern #IndianMonsoon #HealthEffects #GlobalImpact #WeatherMysteries #ClimateCrisis #ExtremeWeather #naturaldisasters
Add a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment